SparkToro analyzes a random sample of 2,000 of your Twitter followers and tries to estimate how many are fake. I did OK (love the spike at 9 out of 10), and given the methodology I think the 12% fake number is probably a slight over-estimate..
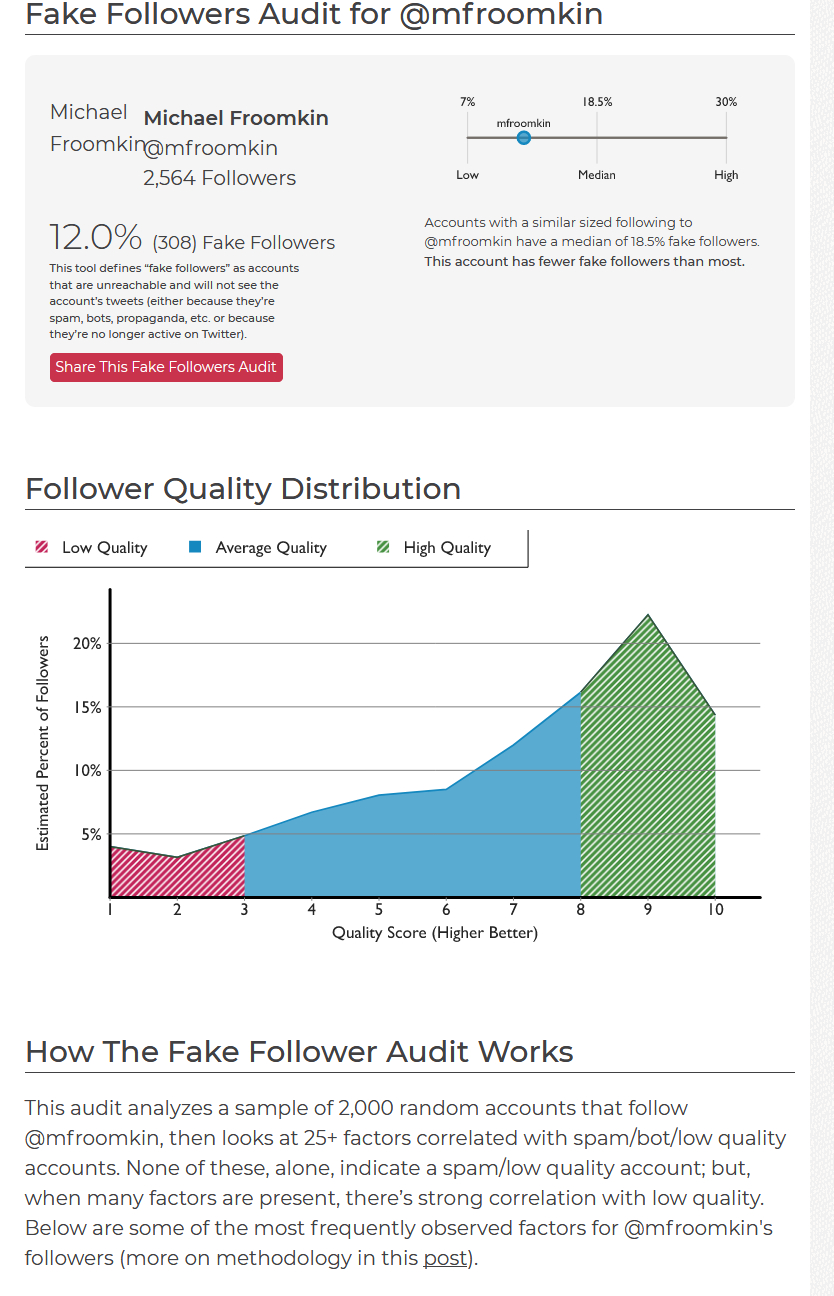
SparkToro analyzes a random sample of 2,000 of your Twitter followers and tries to estimate how many are fake. I did OK (love the spike at 9 out of 10), and given the methodology I think the 12% fake number is probably a slight over-estimate..

At UM’s Data Privacy Day event I made 10 suggestions about what you can do to protect your e-privacy and autonomy. Here they are:
(Some links added after original posting)
 Ok, maybe FF57 is faster, but it’s uglier and less functional. They finally pulled the trigger and killed off thousands of add-ons. My workflow just got noticeably worse.
Ok, maybe FF57 is faster, but it’s uglier and less functional. They finally pulled the trigger and killed off thousands of add-ons. My workflow just got noticeably worse.
I just lost about 30 enhancements and extensions. Admittedly, many were just frills. But I’ll particularly miss Tab Mix Plus, Autocopy, CoLT, Tab Mix Plus, Zoom Page and the beautiful and functional Nautipolis theme.
Oh, and did I mention I’m missing Tab Mix Plus?
With this revision and the disabling of key customizations, FireFox eliminates its #1 advantage over Chrome. After all these years, I may just switch.
Google Takeout–I didn’t know this was even possible, but you can download a copy of your email, contacts, calendar, google drive, and indeed everything google, in .zip format. Alas there is no way obvious way to automate it. So do it right away, or you’ll forget.
Thank you to Stefan Krasowski for the pointer.
Several months ago, Chrome started experimenting with adding suggested articles to your new tab page. That was neat when it was optional. In the new Chrome 54, it’s mandatory. Here’s how to turn it off.
When you open a new tab in Chrome 54, if you scroll down you’ll see recently used bookmarks, followed by a list of suggested articles (the same one Google Now shows you that can be a little bit of an echo chamber). If you’re not a fan, open both of the following settings in Chrome and disable them:
chrome://flags/#enable-ntp-popular-sites
chrome://flags/#enable-ntp-snippets
You may have to restart the browser for it to work. Once it’s done, however, those suggested articles should be gone. Enjoy your clean new tab page!
The Attorney Generals of four right-wing states sued today to block the transfer of the US’s control over IANA to ICANN. Here’s a link to the plaintiffs’ complaint and request for declaratory and injunctive relief.
And here’s my very quick take on the lawsuit: The APA claim is bogus. I think they lack standing for the property claim. The property claim is also meritless, as the government is not giving away any property it “owns”. The US is letting go of a contractual right to veto alterations to the data in a computer file (the root zone file) held on a privately owned machine. There is no intellectual property right because the contents of the file are in the public domain, and US law would not recognize this as a compilation copyright. What’s at issue in the IANA transfer is the loss of the US government’s right to veto authoritative changes to the file, not to own the contents.
In any case, the proposed transfer doesn’t harm the defendants in any way now, and their complaint fails to say that it does. Plaintiffs only give extremely speculative allegations of possible future damage. Indeed, the most they can come up with in para 22 of their complaint is that “Plaintiffs will lose the predictability, certainty, and protections that currently flow from federal stewardship of the Internet and instead be subjected to ICANNs unchecked control.” While I am more sympathetic than most about the dangers of being subject to ICANN’s unchecked control, the fact remains that in the absence of any clear threat by ICANN do something that would harm the plaintiffs in some way this is far too speculative a harm to be recognized by a US judicial system that is allergic to speculative harm. The same argument applies to the claim that ICANN might – no sign at all it will – increase fees to GSA for .gov, which might – no clear sign it would – be passed on as a cost to the plaintiffs. (para 29).
More generally, the complaint takes a surprisingly collectivist view of private property given that it was filed by some of the more right-wing state officials in the land. My computer is not a public forum. Yet, by claiming that “the internet” has been “established” by the US as a public forum, the plaintiffs seem to want to (in effect) nationalize every computer on the Internet, or at least all the US ones. See for example paras 32 and 35-36 of the complaint which refer to the private use of private computers, but try to turn the computers and the uses into something that requires licenses or which government could control.
Count 3 is bogus because the Commerce Department’s act isn’t a rule in either form or substance. It might arguably be an adjudication – I wrote an article arguing that other related actions should be seen as adjudications (but the courts didn’t bite). NTIA has always taken the view that changes to the IANA relationship are just contract negotiation, like buying paperclips, and those don’t require notice and comment and are not adjudications either; instead it’s just purchasing (I thought the $0 cost of the purchase orders was odd, but that failed to convince enough people.) In any case, not renewing the contract is even less an action than altering it.
Count 4 – the claim that the government is lacking statutory authorization for its actions – is a little more interesting. It has two problems, however: first, the plaintiffs lack the standing to bring it. Second, if it is correct, it likely proves too much, for if getting rid of the Root Zone File was lacking authority, so too was maintaining it. So were this to go forward, the result would be to say the government couldn’t do any of the things it has done in the ICANN/IANA space … which is exactly the result that the plaintiffs are suing to prevent.
Count 5, the tortious interference with contractual relations claim, founders on the absence of any non-speculative damages. US tort law requires you have damages to prevail on a tort claim.
In the long run, this claim cannot succeed. Whether the parties might be able to scare a judge into throwing a spanner in the works while he or she figures things out, I don’t know, but even if they do I just don’t see any way for this lawsuit to prevail in the long run.